![]()
Accessibility Connections
- For accessibility in online learning and education, join the UDAT working group.
- Attend one of the Digital Accessibility Liaisons' monthly trainings.
- Connect with us on ASU's #accessibility Slack channel.
One of the most effective ways to make PowerPoints accessible is to use the default layouts to create new slides. This ensures the content is in the correct reading order and has proper titles. Do not create new text boxes on slides (unless you're willing to check and edit the reading the order of the objects).
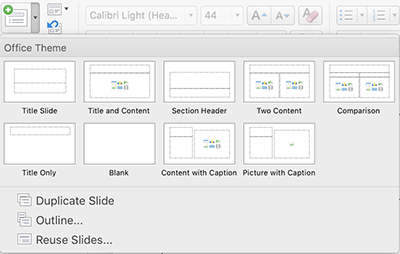
If you'd like a different layout for an existing slide, do not create a new text box. Instead, change the layout:
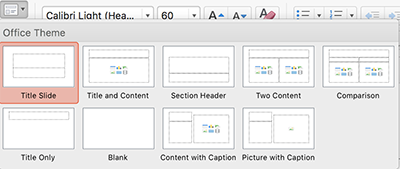
If you must add additional content to a slide, you will need to check the reading order of the objects.
The Selection Pane will display in the right-hand sidebar. Drag the objects into the order you want them to be read. Note: The reading order for objects listed in the Selection Pane is from bottom (first) to top (last). (The numbers indicate the order in which the object was added.)
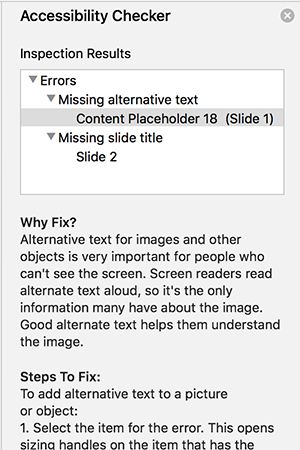
Missing slide titles are one of the biggest accessibility barriers with PowerPoint presentations.

All images must have an ALT tag. In addition, images that convey meaningful information must have alternative text that describes them. Alternative text may be added in a caption, within the slide text, or in the image's ALT tag.
To add alternative text to the ALT tag of an image:

Decorative images are those used for visual effect only (eye candy). Decorative images and images described elsewhere (for instance, in a caption or in the content of the slide) should be marked as decorative by selecting the checkbox (Windows) or a toggle (mac) in the alt text panel on the right. Leave the text box empty. 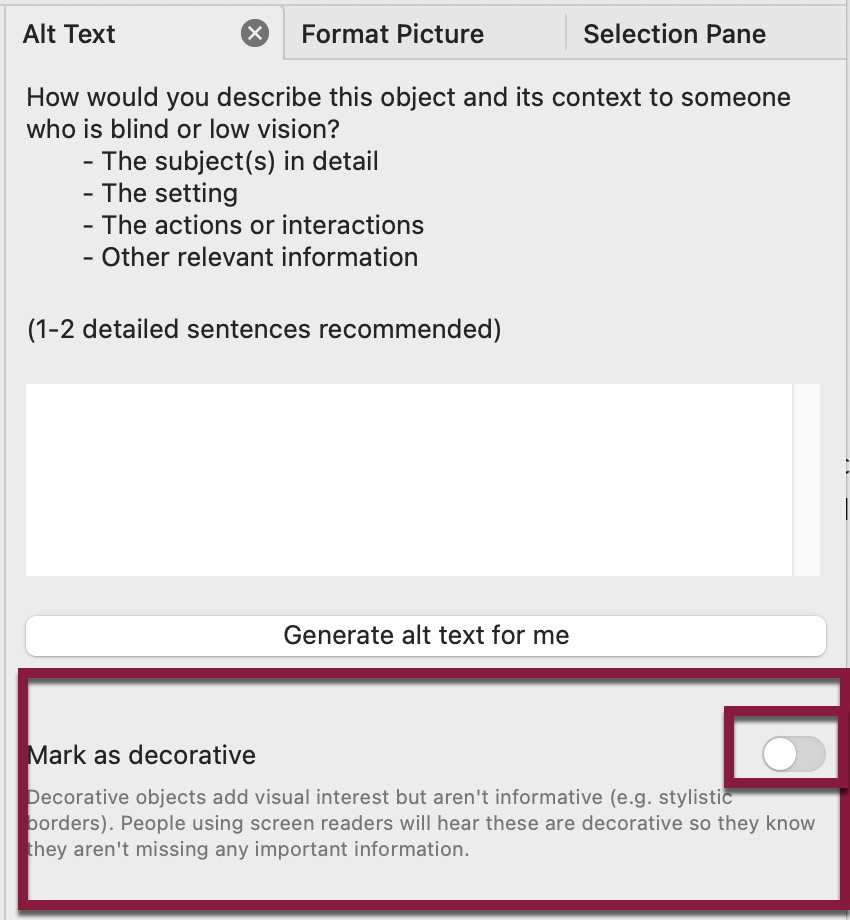

Left image: Mac
Right image: PC
For more on which images need alternative text and how to write effective ALT text, see "Images: Alt Text."
We recommend always creating charts in PowerPoint to take advantage of an important accessibility feature. Like images, most charts are not accessible to screen readers; however, charts built within PowerPoint have corresponding data tables that are accessible and can be added to the slide.
To create a new chart in PowerPoint:
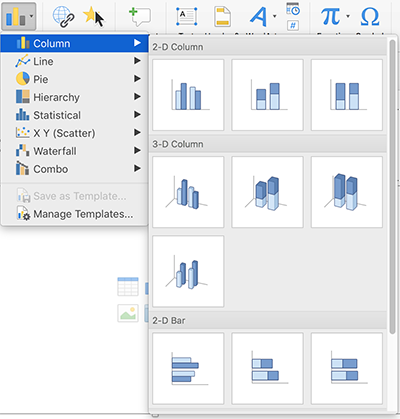
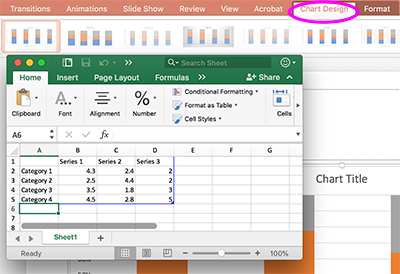
Because charts are images, you must an ALT text to it. For charts that have a corresponding data table, add an empty ALT tag by following the instructions in #3 above. If you haven't supplied alternative text elsewhere on the slide, add alternative text describing the chart to the ALT tag, as explained in #3 above.
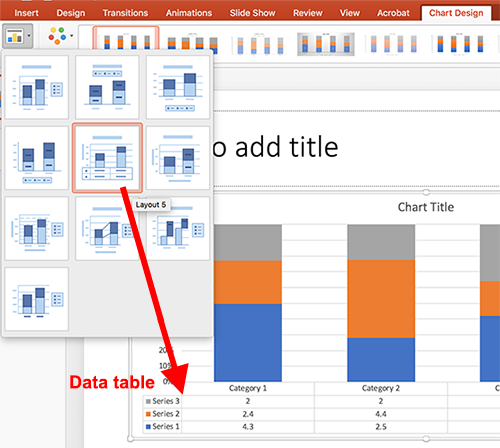
To add a new data table to a slide, always use Insert Table. On the Insert tab, click Insert Table.

To make videos accessible in PowerPoint, post a link to a version of the video with captions (for instance, to a copy of the video on YouTube). You can embed videos with captions from MediaPlus. Also, make sure to provide a transcript file for the video (a transcript can be generated in YouTube and MediaPlus).
For animations and videos that convey important information visually without spoken narration, provide audio descriptions of the visual content. If the video is embedded in a presentation (e.g., PowerPoint), include the descriptions in the Speaker Notes pane so screen reader users or presenters can access and share that information with individuals who are blind or have low vision.
The Microsoft Accessibility Checker is very useful for finding accessibility problems with MS Office files. We highly recommend running the checker over your slides before publishing them. If issues are found, step-by-step instructions are provided for fixing them.
To run the MS Office Accessibility Checker:


Left image: Mac
Right image: PC
Read more about the Microsoft Office Accessibility Checker.
If you need to create a PDF of a Microsoft PowerPoint file, follow the detailed instructions on how to make accessible PDFs from created documents.
Note: Never use "Print as PDF" to create a PDF from any software or browser. The resulting PDF is not accessible.
When you are presenting to an in-person audience, you can enable auto-captions, as well as subtitles in another language. will appear directly on your slides. This can be helpful if there's a lot of competing noise in the environment or for audience members who are hard of hearing or who speak another language.

Follow Micorsoft's instructions for enabling captions and subtitles in PowerPoint for Windows, Mac and Web.
Note: PowerPoint auto-captions do not meet ADA requirements for accommodations. If you get a request for accommodations:
![]()